 | WEB PAGE OF C.K.MOHAMED TELLICHERRY |

What you need to know
 | WEB PAGE OF C.K.MOHAMED TELLICHERRY |

What you need to know
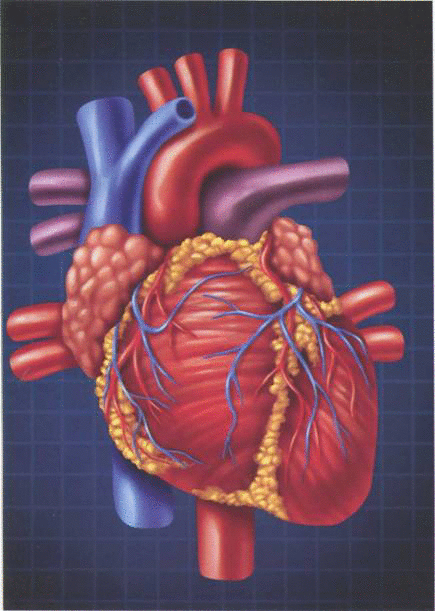 |
Cardiovascular disease - What you need to know
"Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) is the number one cause of death in the developed world, directly responsible for more than 1 7 million deaths each year. CVD is the name given to a range of disorders that affect the arteries of the body, potentially leading to a heart attack, stroke or angina," explained Dr Abdurrazzak Gehani, Senior Consultant Cardiologist at HMC's Heart Hospital. CVD refers to the narrowing, or complete blockage, of any of the arteries in the body, but most importantly the coronary arteries that supply the heart and the cerebral arteries in the brain.
"CVD is projected to increase substantially by 2020 in the Middle East, probably more so here than in other regions of the world due to escalating risk factors," Dr Gehani added.
What is angina?
The term angina stems from the Latin angere, meaning to strangle or choke. Angina is caused by reduced blood flow through the coronary arteries (the arteries that transport blood and oxygen to the heart). This reduced flow is usually due to the deposition of cholesterol fats on the walls of these arteries. These deposits lead to a narrowing of the arteries and restricts blood flow to the heart. When blood flow is significantly reduced it can lead to chest pain, known as angina. Angina usually starts with physical exertion, such as walking uphill, when the heart muscle works harder and requires more blood. At first, the anginal chest pain often improves with rest, but as the narrowing increases, pain may be experienced even at rest and may take much longer to be relieved. These features are important warning signs that a person's coronary artery disease is getting significantly worse.
|
|||
 |
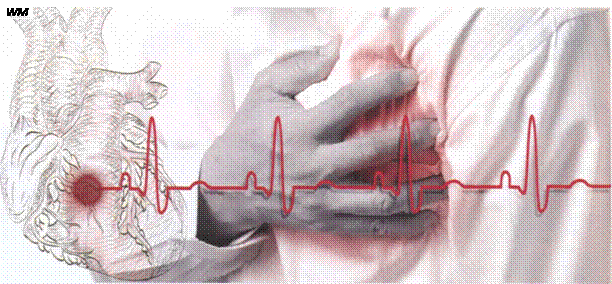
What is heart attack?
A heart attack occurs when the vessels that supply oxygenated blood to the heart become completely blocked. This usually occurs when a blood clot develops on top of the fatty deposits and severely reduces blood flow. The pain is usually much more severe and prolonged than in angina and even occurs at rest. Many patients also feel weak, sweaty and dizzy or may even lose consciousness. What is a stroke? A stroke can occur when the blockage affects one of the arteries that supply the brain with oxygen and nutrients. These blockages are caused in a similar way to those leading to heart attacks through a build-up of fatty deposits narrowing the artery walls, followed by clotting of the blood inside these arteries. What are the risk factors that contribute to the development of CVD? The risk factors can be put into two categories; those that we have control over - controllable risk factors - and
those which cannot be influenced -uncontrollable risk factors.
Uncontrollable risk factors:
Age:
The risk of developing CVD increases with age, with a significant increase for people more than 50 years old.
Gender:
Men are statistically more likely to develop CVD than women.
Race:
Certain ethnic groups are more at risk of developing CVD than others. For example, in the United States CVD is far more prevalent in African Americans than in Caucasians.
Family history:
The risk of developing CVD is greatly increased when there is a family history of the disease.
|
|||
 |
SMOKING:
Cigarette smoking is one of the leading risk factors for CVD with 40 percent of all smokers dying from the disease. Smoking increases the narrowing of the arteries, leading to restricted blood flow to the heart and brain. Smoking can also cause clotting of the blood inside these arteries,
causing a heart attack or stroke. Additionally, smoking can lead to heart attacks in young people, even before the development of fatty deposits in the arteries.
SATURITED FAT INTAKE: Saturated fats are those derived from butter, ghee, coconut oil, palm oil etc. A diet high in saturated fat significantly contributes to the build-up of fatty deposits on the artery walls. Animal meat and dairy products all contain substantial levels of saturated fat. Conversely, unsaturated fats such as olive oil and corn oil are healthier and should be used whenever possible.
HIGH CHOLESTEROL: High levels of 'bad' cholesterol (LDL) in the blood will increase your risk of CVD. This should be differentiated from the HDL form, which is the healthy, protective cholesterol. To maintain healthy cholesterol levels it is important to limit the intake of saturated fat and cholesterol in your diet. High (LDL) cholesterol is not only present in obese people. Many people with a healthy weight have genetically inherited the problem of high cholesterol from their family.
HYPERTENSION: High blood pressure hardens the arteries and places extra strain on the heart. It must be stated that most people who have high blood pressure do not feel any symptoms until they develop angina, stroke or a heart attack. Therefore, it is important to check your blood pressure regularly, especially if there is a history of high blood pressure in your family.
High blood pressure and cholesterol are often referred to as 'SILENT KILLERS' as they produce no symptoms
HIGH SALT INTAKE: A high intake of salt may lead to high blood pressure. Avoid snacks with a high salt content such as crisps, fast food and many canned and ready-made meals. Also, only add salt to your meals when absolutely necessary.
DIABETES:
Raised blood sugar - due to its subsequent complications on the arteries - is an important risk factor for the development of CVD. Controlling body weight, exercising regularly
and correctly using medications for lowering blood sugar, such as insulin, can reduce the risk. It is important for diabetics to note that all other risk factors such as smoking, hypertension and high cholesterol become even more dangerous. Therefore, diabetics must not only control their diabetes, but also reduce these associated risk factors.
LACK OF EXERCISE:
Regular exercise helps to maintain a healthy weight, improves fitness and strengthens the heart and lungs. It can also reduce blood pressure and cholesterol. Exercising at least three or four times a week, performing an activity that raises your heart rate, will reduce your risk of CVD. Exercise also raises the level of good cholesterol.
LOW INTAKE OF ANTIOXIDANTS:
Antioxidants - found in large quantities in fruit, vegetables and nuts - are molecules that fight the development of disease and help to neutralize the harmful effects of saturated fat. Specifically in relation to CVD, antioxidants help to break down the fatty deposits that build up on the artery walls, keeping the passageway clear to allow a strong flow of blood.
LACK OF REGULAR SCREENINGS:
Regular screenings are essential in order to assess your current risk of CVD. Your doctor will be able to monitor your
weight, blood pressure, blood sugar level and cholesterol level to identify abnormal values and advise whether you need to make lifestyle changes. High blood pressure and cholesterol are often referred to as 'silent killers' as they produce no symptoms. Without regular screenings for blood pressure and cholesterol it is very difficult for people to know if they are at a high risk of CVD.
"While you cannot change your uncontrollable risk factors, it is still very important to be aware of them. People with a high risk of CVD due to their age, gender, race or family history must be extra vigilant when it comes to addressing the controllable risk factors. Healthy eating, regular exercise and healthy lifestyle habits are, as with most diseases, the best prevention for CVD," concluded Dr Gehani.
DID YOU KNOW?
One person dies every 30 seconds from CVD in the US, that's more than 2,600 people every
" |
|||